Embarking on an exploration of 1 define business inventories, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of this fundamental concept. Delving into its multifaceted nature, we’ll illuminate the significance of maintaining optimal inventory levels and unravel the strategies that underpin effective inventory management.
From understanding the diverse types of business inventories to deciphering the impact of inventory valuation methods on financial statements, this guide empowers you with a panoramic view of this critical business function. Join us as we navigate the labyrinth of inventory control and monitoring practices, highlighting the importance of inventory accuracy and visibility.
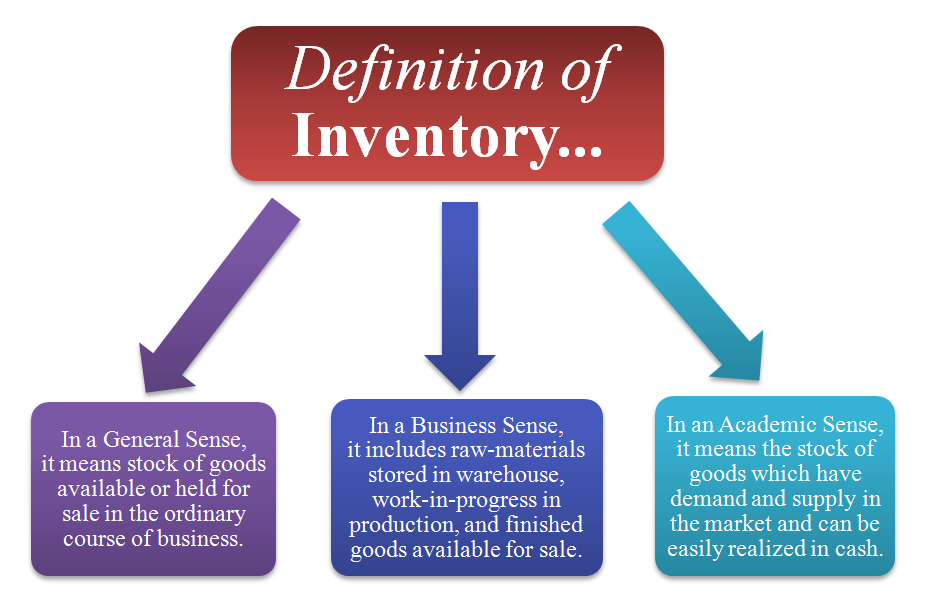
Define Business Inventories: 1 Define Business Inventories

Business inventories refer to the stock of goods and materials held by a business at a particular point in time. They are an essential part of business operations, as they represent the goods that a business has available for sale or use in its operations.
There are three main types of business inventories:
- Raw materials: These are the basic materials that are used to produce a product.
- Work-in-progress: These are products that are still in the process of being produced.
- Finished goods: These are products that are ready to be sold to customers.
The level of inventory that a business holds is important for a number of reasons. Too much inventory can tie up cash and lead to storage problems, while too little inventory can lead to stockouts and lost sales. Businesses must carefully manage their inventory levels to ensure that they have enough inventory to meet demand without overstocking.
Importance of Business Inventories
Maintaining optimal inventory levels is crucial for businesses to ensure smooth operations, meet customer demand, and maximize profitability. Inventories play a vital role in various aspects of business operations, including production, sales, and financial management.
Contribution to Business Operations
Inventories contribute to business operations in several ways:
- Production:Inventories provide raw materials and components necessary for production processes, ensuring uninterrupted operations and meeting production schedules.
- Sales:Inventories enable businesses to meet customer demand by having products available for sale. Optimal inventory levels minimize stockouts, prevent lost sales, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Financial Management:Inventories represent a significant portion of a business’s assets and impact financial statements. Proper inventory management optimizes cash flow, reduces holding costs, and improves financial performance.
Inventory Management Strategies
Inventory management strategies are essential for businesses to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Different strategies have varying benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the one that best aligns with the business’s specific needs and goals.
Common inventory management strategies include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale. This reduces storage costs and the risk of obsolescence, but it requires a high level of coordination with suppliers.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Inventory:FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. This helps prevent spoilage or obsolescence, but it can lead to higher storage costs if the oldest items are not sold quickly.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) Inventory:LIFO assumes that the newest inventory items are sold first. This can reduce taxable income in inflationary periods, but it can also lead to higher storage costs if the oldest items are not sold quickly.
- Periodic Inventory System:A periodic inventory system involves physically counting inventory at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly. This provides a snapshot of inventory levels at a specific point in time, but it can be time-consuming and disruptive to operations.
- Perpetual Inventory System:A perpetual inventory system uses software to continuously track inventory levels in real time. This provides more accurate and up-to-date information, but it can be more expensive to implement and maintain.
Inventory Valuation Methods
Inventory valuation methods determine the value of inventory on the balance sheet. They impact financial statements by influencing the cost of goods sold, gross profit, and net income.
Weighted Average Cost Method
The weighted average cost method calculates the average cost of each inventory item by dividing the total cost of inventory by the total number of units. This method assumes that all units in inventory are equally valuable.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Method, 1 define business inventories
The FIFO method assumes that the first units purchased are the first to be sold. This method results in the cost of goods sold being based on the oldest inventory costs.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) Method
The LIFO method assumes that the last units purchased are the first to be sold. This method results in the cost of goods sold being based on the most recent inventory costs.
Specific Identification Method
The specific identification method assigns a specific cost to each inventory item. This method is often used for high-value or unique inventory items.The choice of inventory valuation method depends on factors such as the nature of the inventory, the industry, and tax implications.
Inventory Control and Monitoring
Inventory control and monitoring practices are essential for businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, minimize waste, and ensure the accuracy and visibility of their inventory data. Effective inventory control systems help businesses track the movement and storage of inventory items, identify discrepancies, and make informed decisions about inventory management.
Inventory Control Techniques
Inventory control techniques are methods and tools used to manage and track inventory levels. Some common inventory control techniques include:
- Periodic inventory counts:Regular physical counts of inventory items to verify accuracy.
- Cycle counting:Continuous inventory counting process where a small portion of inventory is counted regularly.
- Barcoding and RFID tags:Automated identification technologies used to track inventory movement and location.
- Inventory management software:Computerized systems that track inventory levels, transactions, and other data.
Importance of Inventory Accuracy and Visibility
Accurate and visible inventory data is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about inventory management. Accurate inventory records help businesses avoid overstocking or understocking, optimize inventory levels, and reduce waste. Visibility into inventory data allows businesses to track the flow of goods, identify bottlenecks, and improve inventory turnover.
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization is the process of determining the optimal level of inventory to hold, taking into account factors such as demand, lead time, and carrying costs. The goal of inventory optimization is to minimize the total cost of inventory, while ensuring that there is enough inventory on hand to meet demand.
There are a number of different inventory optimization techniques, including:
- Safety stock optimization: This technique involves determining the optimal level of safety stock to hold, which is the amount of inventory that is held above the expected demand to protect against unexpected increases in demand or delays in delivery.
- Reorder point optimization: This technique involves determining the optimal reorder point, which is the point at which an order for new inventory should be placed.
- Lead time optimization: This technique involves reducing the lead time for inventory, which is the time it takes to receive new inventory after an order is placed.
Inventory optimization can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced inventory costs: By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can reduce the amount of inventory they hold, which can lead to lower carrying costs.
- Improved customer service: By ensuring that there is enough inventory on hand to meet demand, businesses can improve customer service levels.
- Increased efficiency: By optimizing inventory processes, businesses can improve efficiency and reduce waste.
Summary
In conclusion, 1 define business inventories encompasses a vast array of strategies and practices that are essential for optimizing business operations. By delving into the intricacies of inventory management, businesses can unlock the potential for increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Embracing a proactive approach to inventory management empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace, ensuring that they remain competitive and well-positioned for success.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key benefits of maintaining optimal inventory levels?
Maintaining optimal inventory levels enables businesses to meet customer demand effectively, minimize the risk of stockouts, reduce storage costs, and optimize cash flow.
How do different inventory management strategies impact business operations?
Inventory management strategies influence factors such as inventory turnover, carrying costs, and customer service levels. Different strategies, such as just-in-time inventory or bulk purchasing, are tailored to specific business needs and objectives.
What are the most common inventory valuation methods used by businesses?
Common inventory valuation methods include FIFO (first-in, first-out), LIFO (last-in, first-out), and weighted average cost. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on factors such as industry practices and tax implications.
