Embarking on an exploration of inventory business examples, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of inventory management, providing valuable insights and practical strategies to optimize your operations. Discover the diverse types of inventory businesses, master the art of inventory management, and uncover the latest trends shaping the future of inventory management.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to elevate your inventory management practices and drive business success.
Inventory Management
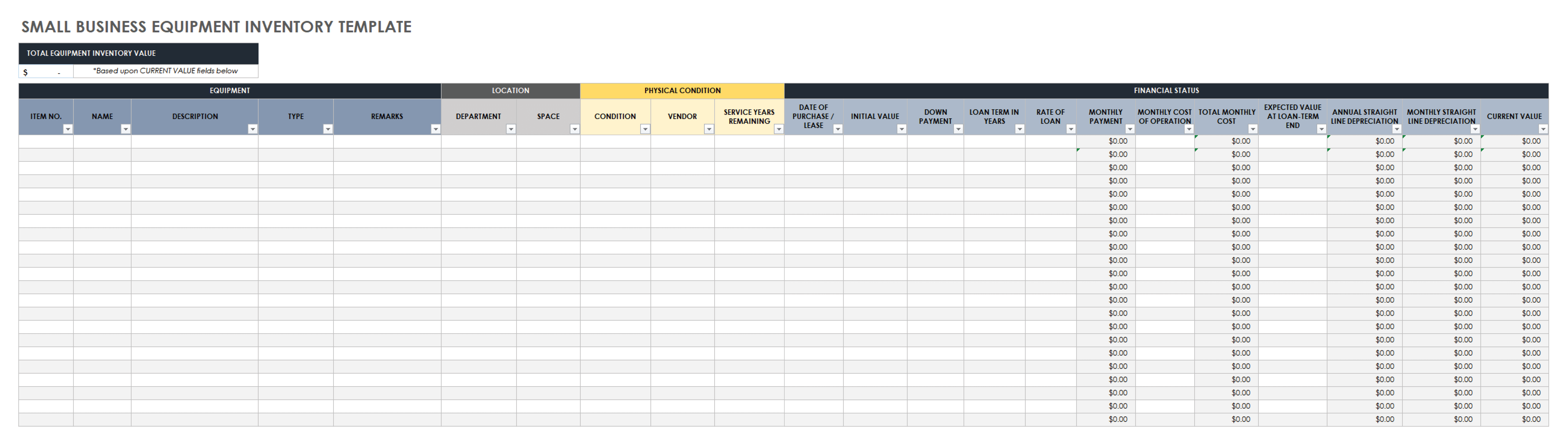
Inventory management is a crucial aspect of business operations that involves overseeing the flow of goods, from procurement to storage and distribution. It ensures that businesses have the right amount of inventory to meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking.
Common Inventory Management Methods, Inventory business example
There are several common inventory management methods used by businesses:
- First-in, first-out (FIFO):This method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, ensuring that goods do not remain in stock for extended periods.
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO):In contrast to FIFO, LIFO assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first.
- Weighted average cost:This method calculates the average cost of inventory by considering all purchases made over a period of time.
- Just-in-time (JIT):JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale.
- Economic order quantity (EOQ):EOQ determines the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time, considering factors such as demand, holding costs, and order costs.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
Effective inventory management brings several benefits to businesses, including:
- Reduced costs:By optimizing inventory levels, businesses can minimize storage, handling, and other inventory-related costs.
- Improved customer service:Effective inventory management ensures that businesses can meet customer demand, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased efficiency:Streamlined inventory management processes can improve overall operational efficiency, reducing lead times and waste.
- Enhanced profitability:By reducing inventory costs and improving customer service, businesses can increase their profitability.
- Reduced risk:Effective inventory management helps mitigate the risk of stockouts, obsolescence, and other inventory-related issues.
Inventory Optimization
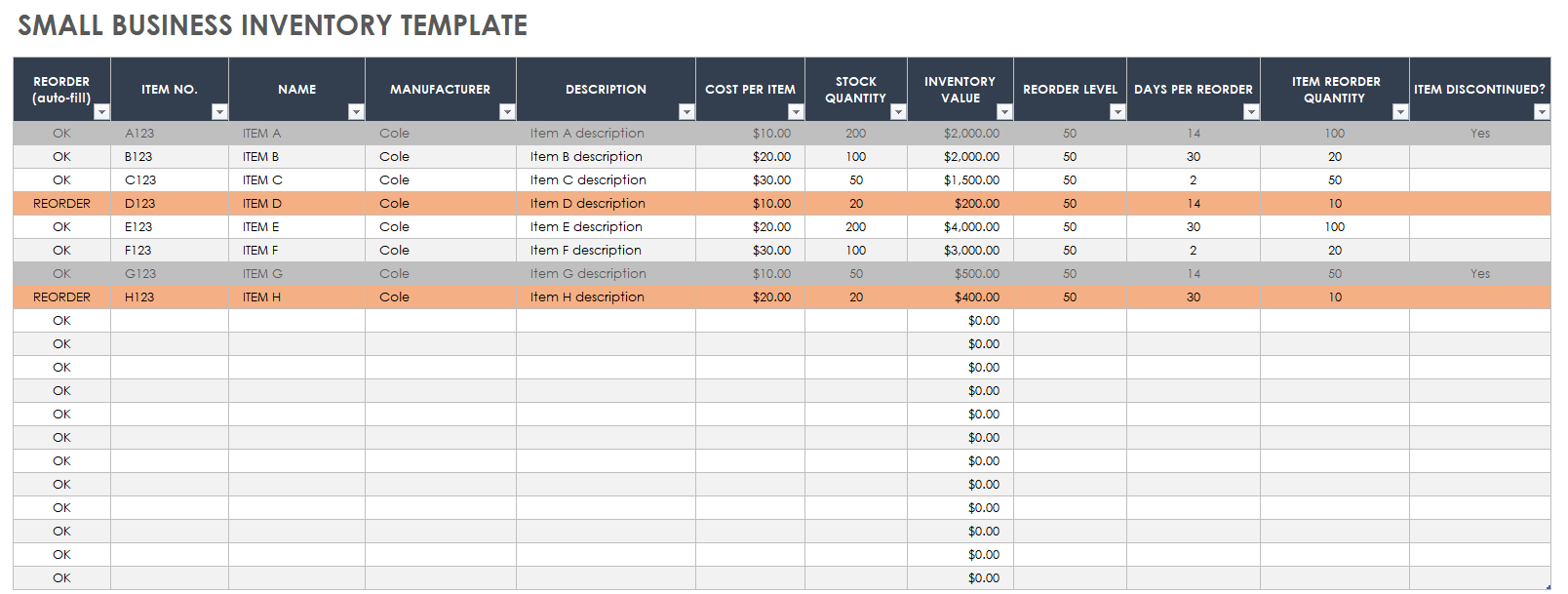
Inventory optimization is the process of determining the optimal levels of inventory to hold in order to minimize costs and maximize customer service. It involves balancing the trade-off between holding too much inventory, which can lead to increased storage costs, obsolescence, and waste, and holding too little inventory, which can lead to stockouts, lost sales, and customer dissatisfaction.
Techniques for Optimizing Inventory Levels
There are a number of techniques that can be used to optimize inventory levels, including:
- ABC analysis:This technique involves classifying inventory items into three categories (A, B, and C) based on their annual usage value. A-items are the most valuable items and should be managed closely, while C-items are the least valuable and can be managed with less attention.
- Safety stock:This is a buffer stock that is held to protect against unexpected increases in demand or supply disruptions. The amount of safety stock that is held will depend on the variability of demand and the lead time for replenishment.
- Economic order quantity (EOQ):This is the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time. The EOQ is calculated based on the demand for the item, the ordering cost, and the holding cost.
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory:This is a system that aims to minimize inventory levels by only ordering items when they are needed. JIT inventory systems require close coordination with suppliers and can be difficult to implement in practice.
Case Studies of Successful Inventory Optimization Strategies
There are a number of companies that have successfully implemented inventory optimization strategies. One example is Amazon, which uses a combination of ABC analysis, safety stock, and JIT inventory to manage its vast inventory. Amazon has been able to achieve high levels of customer service while minimizing its inventory costs.
Another example is Toyota, which uses a system called kanban to manage its inventory. Kanban is a visual system that uses cards to track the flow of inventory through the production process. Toyota has been able to achieve very high levels of efficiency and quality using its kanban system.
Inventory Valuation
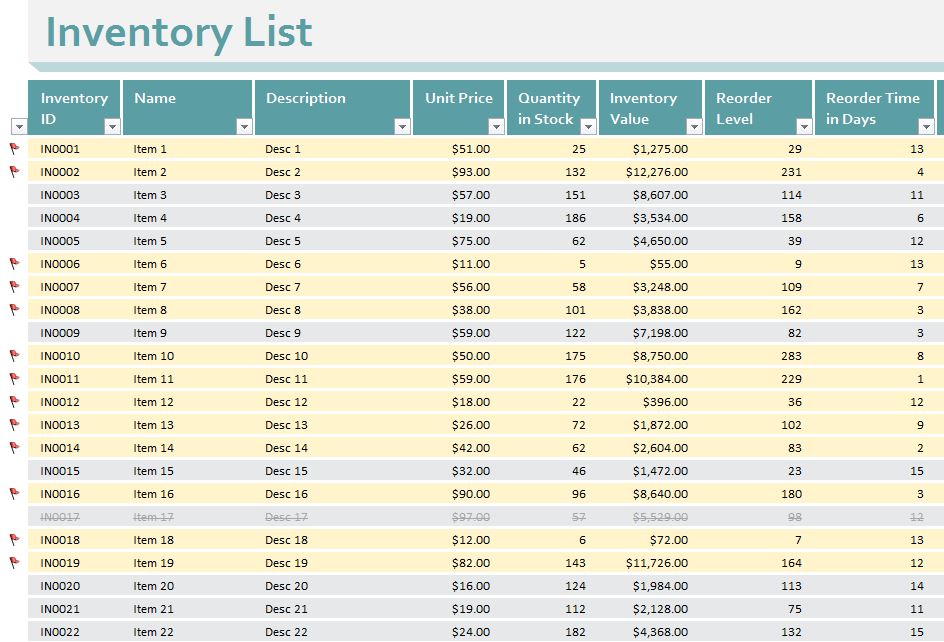
Inventory valuation is a critical aspect of inventory management that involves determining the monetary value of a company’s inventory. Accurate inventory valuation is essential for various reasons, including:
- Financial reporting: Accurate inventory valuation ensures reliable financial statements that reflect the company’s financial health.
- Tax compliance: Inventory valuation affects the calculation of cost of goods sold (COGS), which is a key factor in determining taxable income.
- Decision-making: Inventory valuation provides valuable insights for making informed decisions regarding inventory management, pricing, and production planning.
Inventory Valuation Methods
There are several inventory valuation methods available, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- First-in, First-out (FIFO): This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. As a result, the ending inventory is valued at the most recent purchase cost.
- Last-in, First-out (LIFO): This method assumes that the newest inventory items are sold first. Therefore, the ending inventory is valued at the oldest purchase cost.
- Weighted Average Cost: This method calculates the average cost of all inventory items on hand, regardless of when they were purchased.
- Specific Identification: This method assigns a unique cost to each inventory item, allowing for precise tracking and valuation.
Factors Affecting Inventory Valuation
Several factors can affect inventory valuation, including:
- Purchase Price: The cost of acquiring the inventory items.
- Shipping and Handling Costs: Expenses incurred in transporting and handling the inventory.
- Storage Costs: Expenses related to storing the inventory, such as rent, utilities, and insurance.
- Obsolescence: The potential loss of value due to technological advancements or changes in consumer demand.
- Damage or Theft: Losses incurred due to damage or theft of inventory items.
Inventory Performance Metrics
Inventory performance metrics provide valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of your inventory management processes. By tracking and analyzing these metrics, you can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize your inventory levels and overall supply chain operations.
Some of the key inventory performance metrics include:
- Inventory turnover
- Days inventory outstanding (DIO)
- Inventory accuracy
- Inventory holding costs
- Stockout rate
These metrics can be calculated using the following formulas:
Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Inventory Value
DIO = (Average Inventory Value / COGS)
365 Days
Inventory Accuracy = (Number of Accurate Inventory Counts / Total Number of Inventory Counts)
100%
Inventory Holding Costs = (Average Inventory Value
Holding Cost Percentage) / 365 Days
Stockout Rate = (Number of Stockouts / Total Number of Customer Orders)
100%
By understanding and tracking these metrics, you can gain a comprehensive view of your inventory performance and identify areas where you can make improvements. For example, if your inventory turnover is low, it may indicate that you are holding too much inventory, which can lead to increased holding costs and reduced profitability.
By optimizing your inventory levels and improving your inventory management processes, you can improve your inventory performance and drive business success.
Inventory Technology: Inventory Business Example
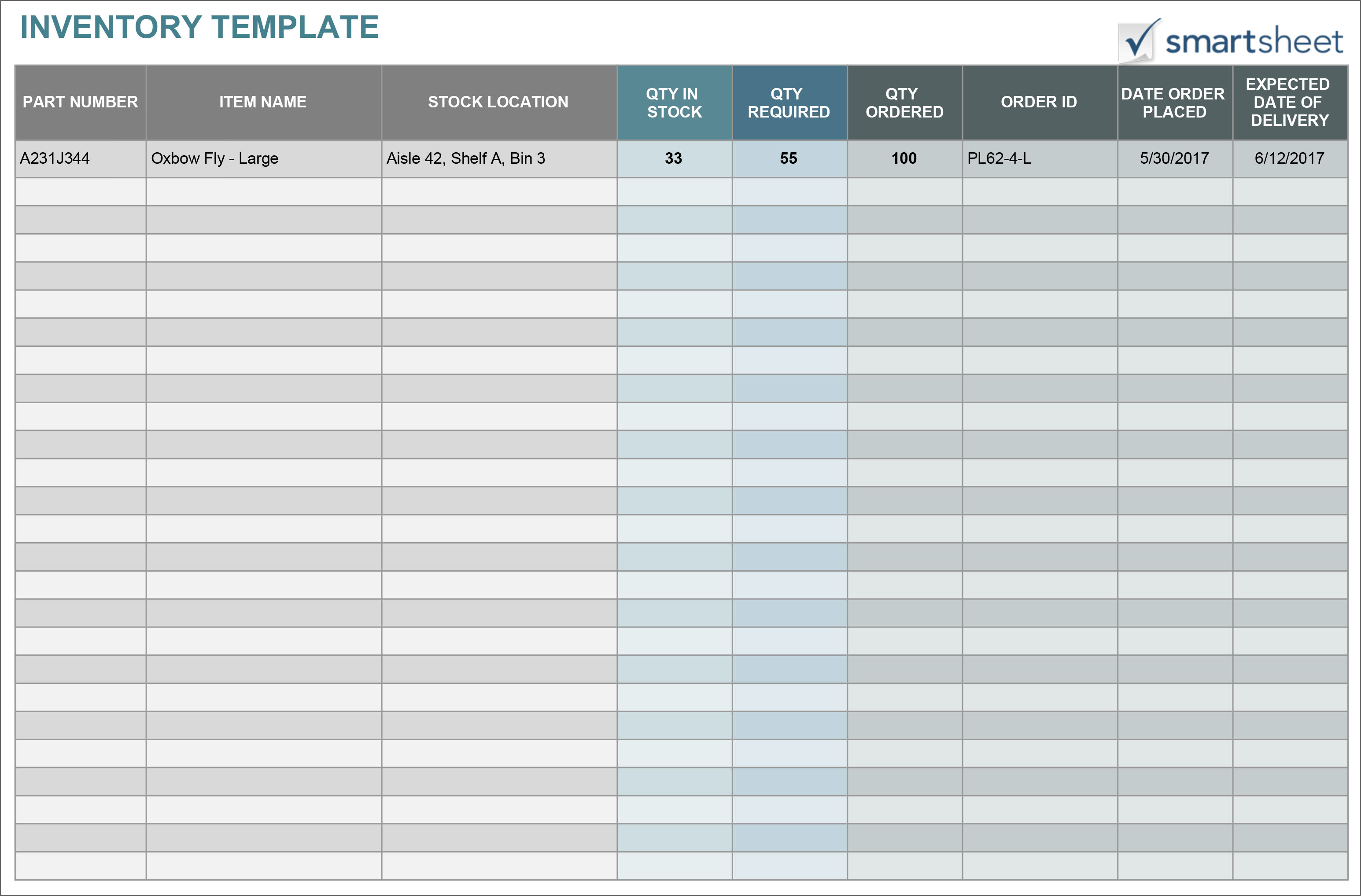
Inventory technology is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of hardware, software, and services designed to help businesses manage their inventory more effectively.
Inventory technology can be used to track inventory levels, manage inventory turnover, and optimize inventory allocation. It can also help businesses to reduce waste, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
Types of Inventory Technology
- Barcode scannersare used to quickly and accurately identify inventory items.
- RFID tagsare small, wireless tags that can be attached to inventory items to track their location and movement.
- Inventory management softwareis used to track inventory levels, manage inventory turnover, and optimize inventory allocation.
- Warehouse management systemsare used to manage the day-to-day operations of a warehouse, including inventory management.
Benefits of Using Inventory Technology
- Improved inventory accuracy:Inventory technology can help businesses to improve the accuracy of their inventory records, which can lead to reduced waste and improved customer service.
- Increased inventory turnover:Inventory technology can help businesses to increase their inventory turnover, which can lead to increased profitability.
- Reduced waste:Inventory technology can help businesses to reduce waste by identifying and eliminating excess inventory.
- Improved customer service:Inventory technology can help businesses to improve customer service by ensuring that they have the right products in stock when customers need them.
- Increased profitability:Inventory technology can help businesses to increase profitability by reducing waste, increasing inventory turnover, and improving customer service.
Case Studies of Successful Inventory Technology Implementations
There are many case studies of successful inventory technology implementations. One example is the case of Amazon.com. Amazon.com uses a variety of inventory technology, including barcode scanners, RFID tags, and inventory management software, to manage its vast inventory.
Amazon.com’s use of inventory technology has helped it to achieve a high level of inventory accuracy, which has led to reduced waste and improved customer service. Amazon.com has also been able to increase its inventory turnover, which has led to increased profitability.
Inventory Trends
The world of inventory management is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. These trends are being driven by a number of factors, including the rise of e-commerce, the increasing complexity of supply chains, and the growing adoption of new technologies.
One of the most significant inventory trends is the shift towards lean inventory management. Lean inventory management is a philosophy that focuses on reducing waste and improving efficiency. Lean inventory managers aim to keep inventory levels as low as possible while still meeting customer demand.
This can be achieved through a variety of techniques, such as just-in-time inventory management and vendor-managed inventory.
Another major inventory trend is the increasing use of data analytics. Data analytics can be used to improve inventory forecasting, optimize inventory levels, and identify trends. This can help businesses to make better decisions about their inventory and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Finally, the growing adoption of new technologies is also having a major impact on inventory management. Technologies such as RFID (radio frequency identification) and IoT (Internet of Things) can be used to track inventory in real time and improve visibility.
This can help businesses to better manage their inventory and reduce the risk of loss or theft.
Future of Inventory Management
The future of inventory management is bright. As new technologies continue to emerge and businesses become more sophisticated in their use of data, inventory management will become increasingly efficient and effective. This will lead to reduced costs, improved customer service, and increased profitability for businesses.
Epilogue
In conclusion, inventory business examples serve as a testament to the transformative power of effective inventory management. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this guide, businesses can unlock operational efficiency, minimize costs, and maximize customer satisfaction. As the industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and leveraging innovative inventory technology will be crucial for businesses to thrive in the competitive landscape.
User Queries
What are the key benefits of effective inventory management?
Effective inventory management can lead to reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, increased efficiency, and enhanced profitability.
What are some common inventory management methods?
Common inventory management methods include FIFO (first-in, first-out), LIFO (last-in, first-out), and ABC analysis.
How can I optimize my inventory levels?
Inventory optimization techniques include demand forecasting, safety stock management, and vendor managed inventory.
